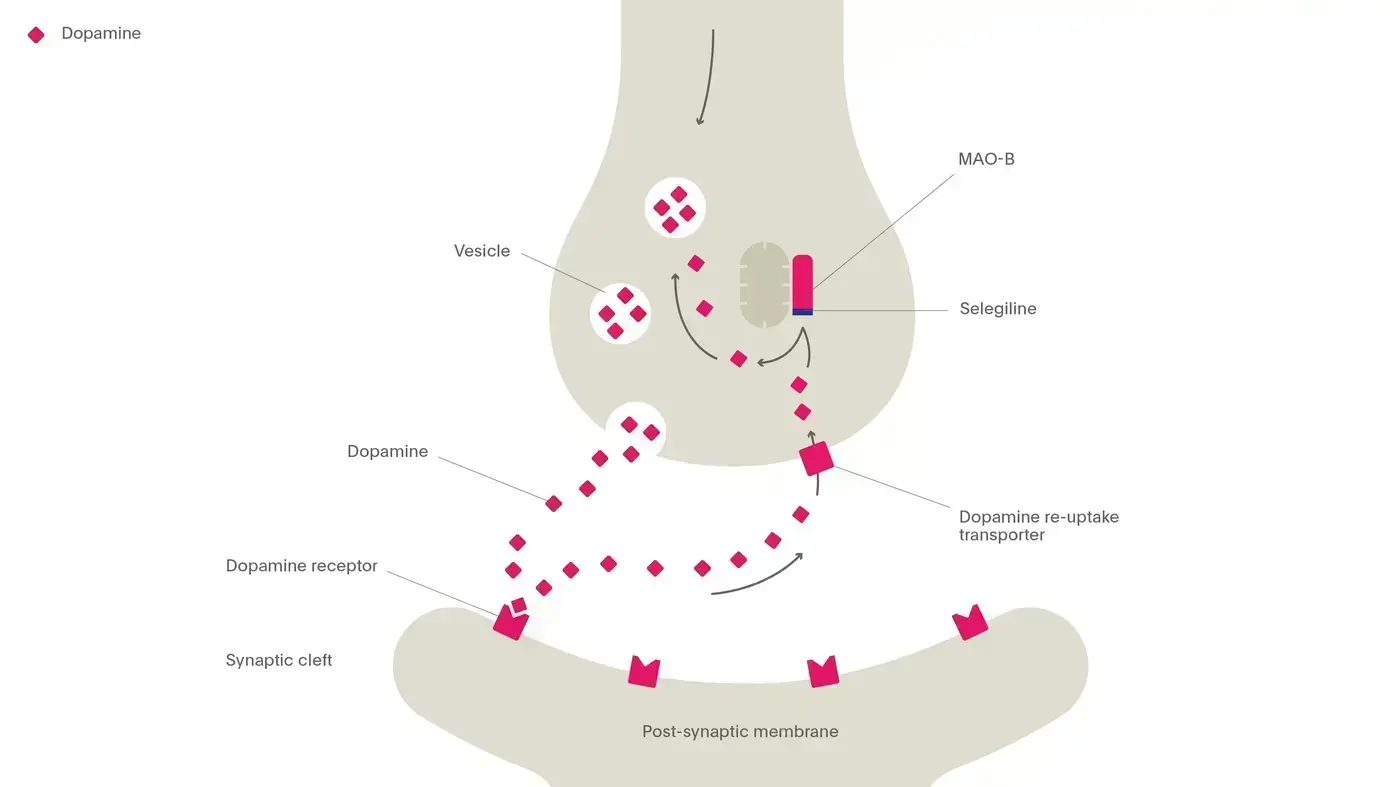
Monoamine oxidase B (MAOB) is an enzyme involved in the metabolism of dopamine. It converts dopamine to its corresponding carboxylic acid via an aldehyde intermediate. MAOB regulates both the free intraneuronal concentration of dopamine and the releasable stores. MAOB inhibitors, such as selegiline, bind to and inhibit MAOB, preventing dopamine degradation. This results in greater stores of dopamine available for release. MAOB inhibitors are used in the treatment of depression. People with depression have lower than normal levels of dopamine and MAOB inhibitors restore the levels to within the normal range.
The mechanism of action of monoamine oxidase B inhibitors